Radon Gas
Introduction, Concerns, and Mitigation Methods
What is Radon?
Radon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally beneath the earths surface. It is colorless, tasteless, odorless, and completely undetectable to humans.
-
- 9 times heavier than air
- Some studies link radon exposure to childhood leukemia.
- At one time, the gas was used for radiotherapy cancer treatment
- Below its −96 °F freezing point, it emits bright yellow luminescence
- It used to be used in spas, when people thought it might confer medical benefits
- Some studies indicate children are at higher risk from radon exposure than adults
Health Risks
| Radon Level | Out of 1,000 non-smokers | Same risk as… |
|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/l | 36 people would get lung cancer | 35 times the risk of drowning |
| 10 pCi/l | 18 people would get lung cancer | 20 times the risk of dying in a home fire |
| 8 pCi/l | 15 people would get lung cancer | 4 times the risk of dying in a fall |
| 4 pCi/l | 7 people would get lung cancer | The same as dying in a car crash |
| Radon Level | Out of 1,000 smokers | Same risk as… |
|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/l | 260 people would get lung cancer | 250 times the risk of drowning |
| 10 pCi/l | 150 people would get lung cancer | 200 times the risk of dying in a home fire |
| 8 pCi/l | 120 people would get lung cancer | 30 times the risk of dying in a fall |
| 4 pCi/l | 62 people would get lung cancer | 5 times the risk as dying in a car crash |
The number of radon deaths each year as estimated by the EPA and Surgeon General.
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
Radon is one of the most comprehensively investigated human carcinogens.
Laboratory studies have documented that an alpha particle can cause both single- and double-strand DNA breaks and can produce indirect genotoxic and nongenotoxic effects on both traversed and neighboring non- traversed cells. Experimental animal exposures to radon clearly demonstrate that radon decay products cause lung cancer.
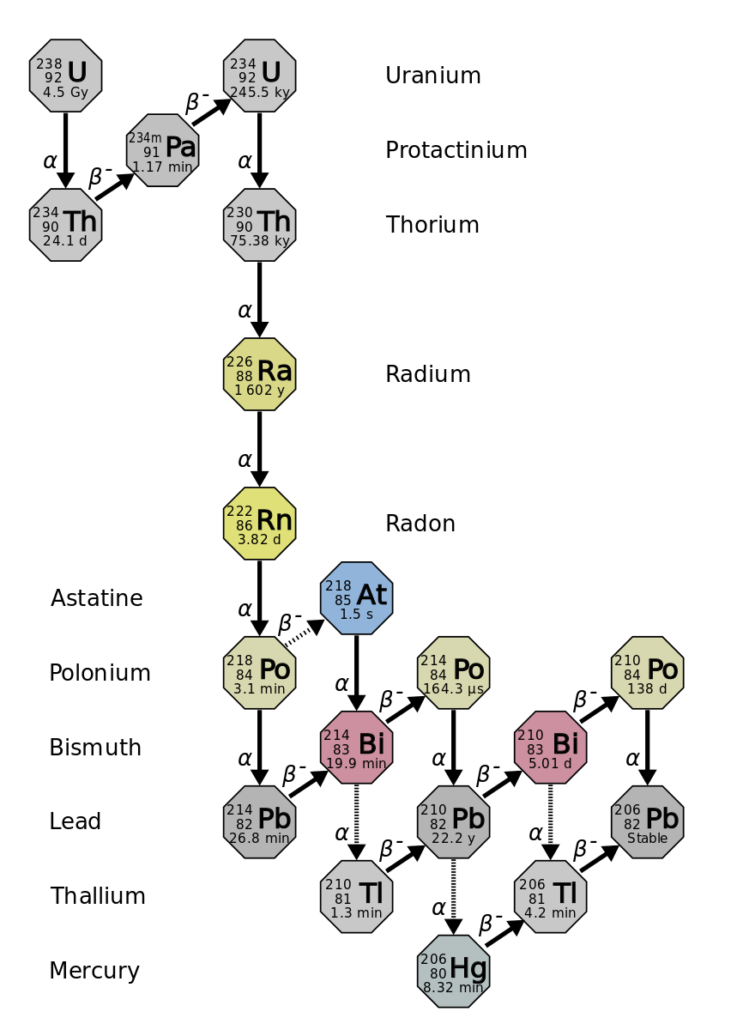
Radon is a radioactive gas.
When the atoms of an element have extra neutrons or protons it creates extra energy in the nucleus and causes the atom to become unbalanced or unstable. Radon is unstable and therefore spontaneously disintegrates into decay products.
Polonium-218 and Polonium-214
Responsible for over 95% of the radiation dose to the lungs, Polonium-218 and Polonium-214 are solid metals with an electrostatic charge. This charge allows them to attach to other airborne particles such as dust where it can then be inhaled into lung and attach to the epithelium.
Half-life of Radon and RDP’s
While the half-life of radon is 3.8 days, the half life of Polonium 218 & 214 is about 2.5-3 minutes. This means that if you could fill your cup up with radon gas then 3.8 days later half of it would’ve decayed into RDP’s.
Radiation Dose
2.5-3 minutes later when Polonium-218 & 214 decay they release ionizing radiation causing mutations in the lung epithelial cells’ DNA.
Why does radiation cause cancer?
Cells respond to the induced damage and attempt to repair it, but sometimes the damage cannot be repaired or is misrepaired, which may lead to mutations. The modifications induced by low levels of radiation dose may be transmitted to daughter cells and may lead to uncontrolled cell growth and consequently cancer, the health effect of primary concern in the context of radiation.
Radon Pathways
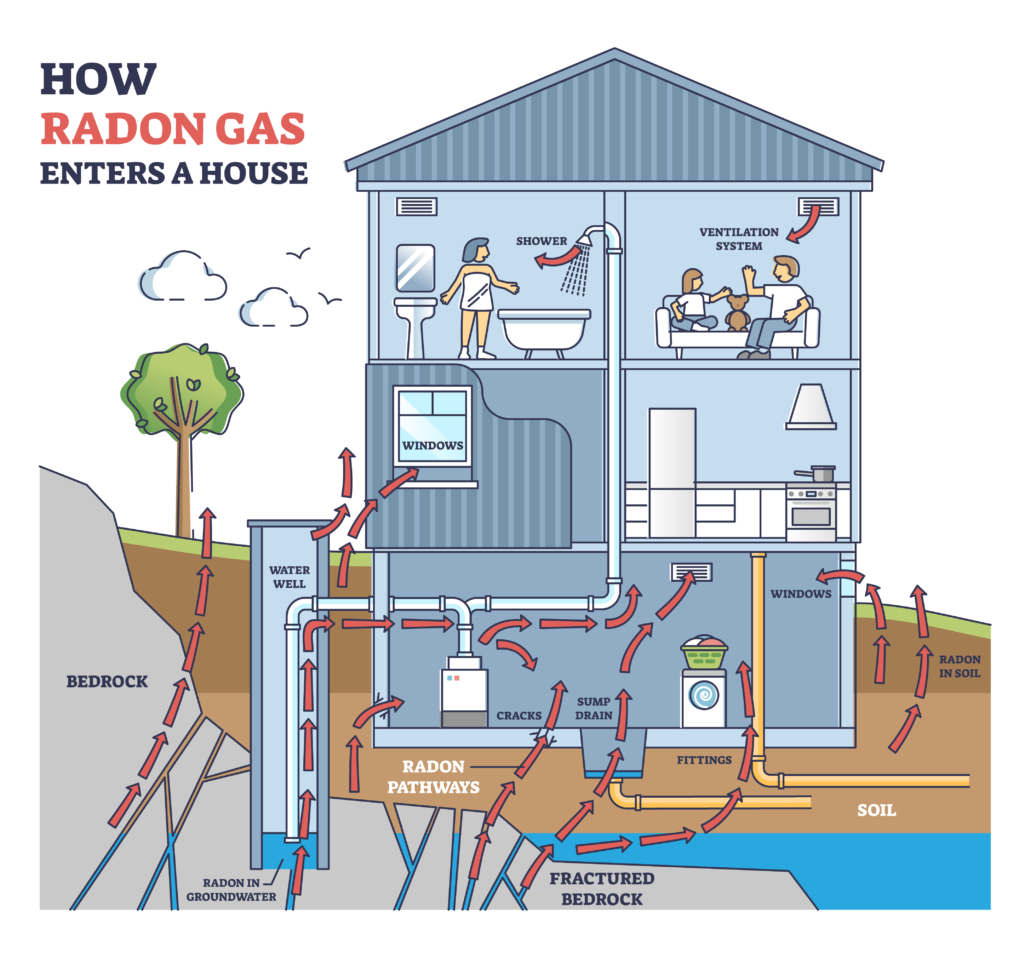
Foundation wall cracks
Basement windows
Sump/Drain tile systems
Floor/Wall penetrations
Cracks in the slab
Water supply
Foundation floor and wall cracks
Radon gas can be pulled through cracks in the foundation.
- Monitoring wall and floor surfaces for cracking.
- Sealing as cracking occurs and monitoring for worsening.
- The floor to wall joint should be sealed if not part of a dewatering system.
Water Supply
Radon can be absorbed by water underground where it can then be pumped into homes.
- Radon in water is rarely a concern for public water supply, however in some instances problems have been found in well water.
- If a radon system is installed and levels are still testing high, your measurement specialist may suggest testing a water sample.
- When water is a pathway for radon, levels will be higher in kitchens and bathrooms where the water is agitated and gas is released.
Wall/Floor Penetrations
Radon gas can be pulled through unsealed penetrations in the walls and floor slab.
- Unsealed penetrations should be sealed and maintained to prevent radon gas entry.
- Sealant tends to break down over time and should be monitored for cracking or deterioration.
Drain Tile/Sump Systems
Drain tile systems provide an efficient way for radon to be pulled into the structure through underground perforated piping.
- Sump pits should be sealed with an air tight lid to prevent radon gas entry.
- Pump discharge lines may penetrate the foundation wall where sealing is also necessary.
Basement Windows
Due to their close proximity to grade level and perhaps sub-grade, radon can be pulled into the structure through basement windows.
- Radon vent terminations should be 2′ above any operable window within 10′ to prevent re-entry.
- Windows should be appropriately sealed and monitored.
Open Soil
Open soil provide an unrestricted radon gas entry.
- Floor drains that drain to soil should have a one way valve installed or be sealed off.
- Shower boxes should be backfilled with sand or gravel and sealed off with either cement or mortar.
- Crawlspaces should have a vapor barrier installed at the soil to seal off the ground from the interior of the structure.
Foundation Type
Any structure can have a source, pathway, and driving force to allow for radon accumulation. This includes new construction, old construction, and foundations of all kinds whether on a basement, crawlspace, or slab.
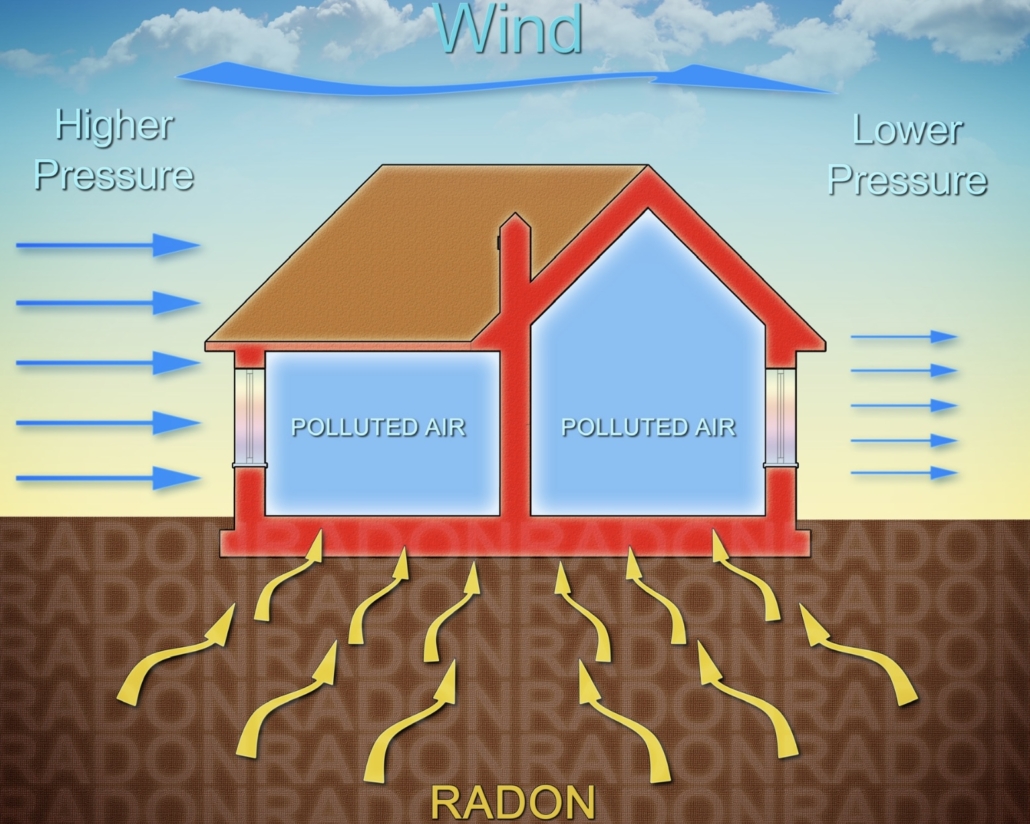
Driving Forces
Wind Pressure
-
Air pressure is greatest on the windward side of the structure.
-
Air pressure is least on the leeward side of the structure.
-
Pressure can be decreased if the leeward side of the structure has more openings, surface area, larger leaks, etc.
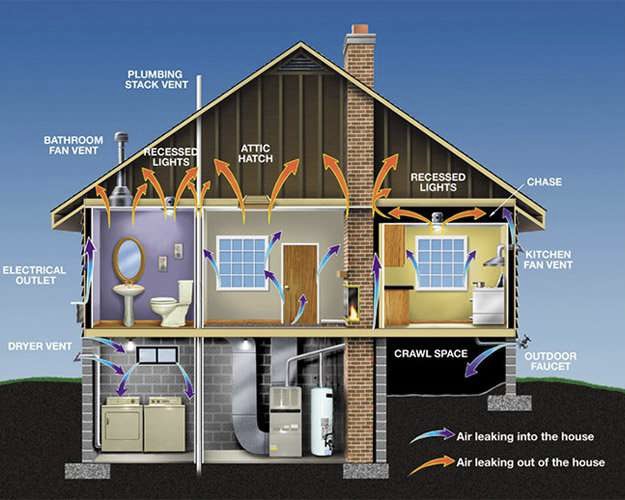
Ventilation Pressure
-
Gas furnaces that draw combustion air from the interior.
-
Ventilation fans such as kitchen, bathroom, and whole house fans.
-
Clothes dryers and central vacuum systems.
Stack Pressure
-
Difference in interior/exterior temperatures.
-
Height of the structure.
-
Air leaks within the structure.
As radon is pulled into the structure it begins to accumulate at the lowest level due to its dense characteristics. As accumulation increases radon concentration levels rise until they meet a point of equilibrium.
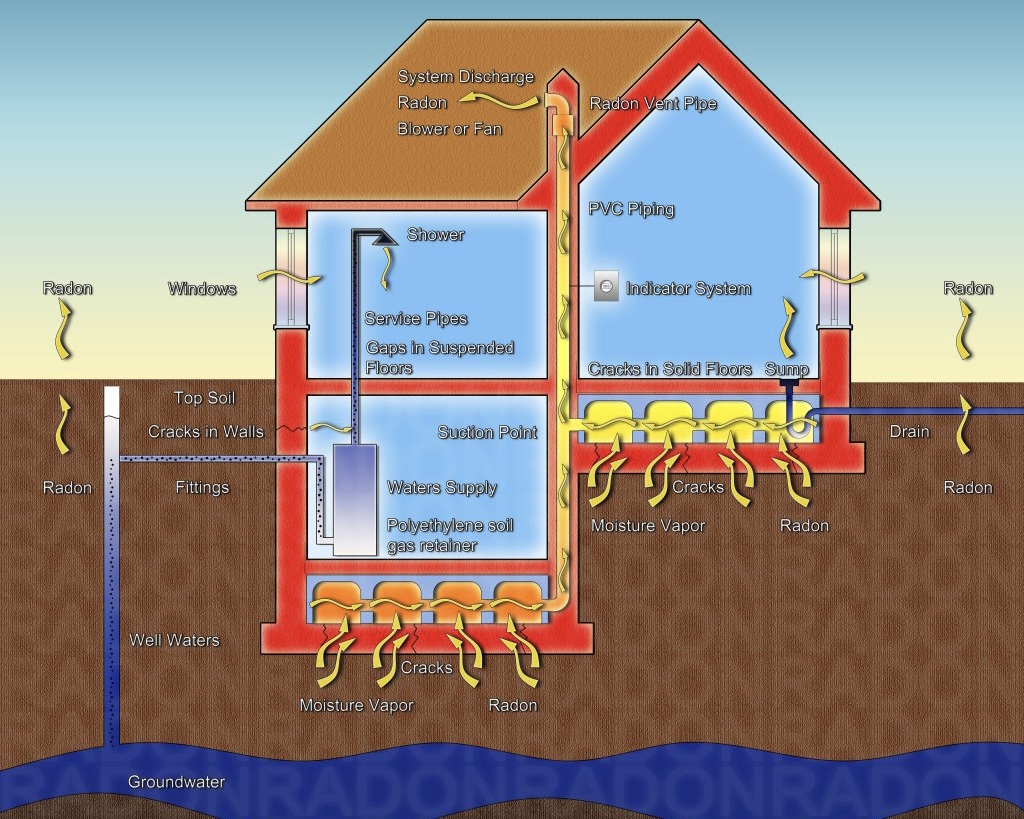
Mitigation System Types
Radon Resistant New Construction
Passive System
Sub-Slab Depressurization
Drain Tile Depressurization
Sub-Membrane Depressurization
Coming Soon…
From Inspection to Closing: A home inspectors approach to real estate inspection contingencies. Leave this class with in-depth insight into the home inspection process, enabling you to effectively manage inspection contingencies and facilitate a smooth transition from inspection to closing.
Coming Soon…
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an ecosystem-based strategy that focuses on long-term prevention of pests or their damage through a combination of techniques such as biological control, habitat manipulation, modification of cultural practices, and use of resistant varieties.
Coming Soon…
Learn the fundamentals of septic systems, including their components, maintenance requirements, and potential red flags to be aware of during the home inspection process. Leave with up-to-date knowledge on modern septic system technologies, regulations, and eco-friendly alternatives.
Course Evaluation

“In this industry time is money, it’s for that reason that I want to express my deepest gratitude for you taking the time to attend one of our CE courses to improve your knowledge and help us all work better together. Thank you so much and have a great day!”
– Matt Utter